Heating metal pipes in a private wooden house. Traditional metal pipes for heating various rooms
If you were asked to make a list of equipment necessary for organizing heating in a private house, then perhaps the only thing that would not cause you any doubt is the pipes. Indeed, pipes are the element that everyone remembers and knows.
There is only one thing left - to follow the modern trends in construction and accurately calculate the required number of these “gray cardinals” of our well-being on long, winter evenings outside the city.
That in heating that everyone knows
The first thing that comes to mind when you need to choose pipes for heating is what material they should be made of.
Actually, the choice here was not long for a long time, but innovations in construction helped to expand this list after all:
- metal pipes - the old and still the most common way of supplying coolant from the boiler to radiators;
- plastic pipes - the gift of innovation, from this ubiquitous polymer - polyvinyl chloride; such pipes are simply called PVC pipes.
Metal Pipes - Yesterday's Reliability
Metal pipes for heating for the home - there is too much range on the market for these means of "transporting" heat. Yes, Gazprom and all of Europe “pray” to them, they are laid along the bottom of the Baltic and will now fight sulfur in the Black Sea. But they can successfully be “greetings” from gas routes and in your home. It will only be necessary to choose a material, because metal is too broad a concept.
Here at our disposal:
- Cast iron pipesas greetings from Soviet times. Frankly, this metal has already "left the stage." For a long time he performed his task and quite successfully.
But it is he who in many respects is the cause of the crazy problems that the housing and communal services of all countries of the former Soviet Union are experiencing today. Corrosion, like corruption (and the words are similar), corrode cast iron pipes and relations between people mercilessly.
We will forget about this metal. You will put such pipes only for exceptional needs, when there is nowhere else to go.
- Steel tubes. Such pipes, and with high-quality performance, do not even look good, but simply brilliant, both literally and figuratively. But it’s rather hard to work with - they weigh decently and require reliable welding.
But it’s much worse that where steel is, there is corrosion, and we come to where we practically started the “thaw”.
- Copper pipes. They can be indispensable if you try to hide the laying of pipes behind false panels and drywall walls.
Copper is surprisingly resistant to external influences. But, frankly, only for those who have nowhere to give money, such pipes are too expensive.

Helpful advice!
Still, do not rule out a situation where you spend the most critical sections of your system from copper pipes.
In the world, besides love (in the soul, by itself), there is no eternal, maybe nothing. But perhaps copper can claim to be used in perpetual motion machines.
In this situation, just be sure to consider the fact that this metal is also a good electrical conductor.
In other words, the use of copper pipes requires very careful electrical insulation and, necessarily, grounding. Remember this, of course.
Life saving plastic
As a solution to the problems of metal pipes - modern plastic PVC pipes.
Such pipes for heating a house have an abyss of advantages:
- Firstly, they are very light, which provides incredible ease of working with them.. Often, such pipes are simply delivered in bays, and this already speaks of their flexibility and the ability, literally "on the fly", to change the configuration of the pipe laying;
- Secondly, PVC pipes are extremely resistant to external and internal influences of any nature.what corrosion is, you will completely forget with these pipes;
- Third, PVC does not know what static electricity is.. This feature is very important for a country house.
The wiring grounding in a major large house is the business of the construction organization, you even know about it, but the struggle “with the static” of a private house is your personal concern. - Fourth. In addition to such a huge number of all kinds of transitional devices that just run up your eyes.
That's where the designers gave vent to their imagination, that's why you will begin to respect them.

Some additional notes about plastic
If it comes to choosing pipes for heating, then of course - PVC, but taking into account some nuances:
- Despite the fact that a huge number of plastic fittings have been developed for pairing pipes, we recommend using reliable copper material for this.
In any other case, you run the risk of truly feeling that not only electronics is the science of contacts, but the pipeline network too; - When we talk about PVC pipes for heating, we do not mean ordinary plastic pipes, they will not withstand the constant effects of high temperatures. This refers to special multilayer pipes with a mandatory inner aluminum layer.
It is these PVC pipes that are used in heating. They often even come with instructions for use.

The most important component is the connecting elements with which the design idea has enriched us in abundance, the main thing is only the selection of a suitable and, necessarily, extremely reliable
A few more nuances of the specific use of PVC pipes in heating systems:
- of course, use only special pipes, but if there is such an urgent need to close the system, and you have only an ordinary PVC pipe at your disposal, you can take a chance and put it on the return stroke of the coolant - from the radiator to the boiler, and better, after the pump, when the coolant has already largely given up its heat;
- the lightness of PVC pipes allows them to be successfully used behind suspended plasterboard ceilings, but on one condition - do not forget that you will need to count on the maximum load capacity of the ceiling structure of 20 kg per square meter, note that the calculation must be done when the coolant is filled system.

Helpful advice!
Another question that arises when choosing pipes for a heating system is their diameter.
It will immediately appear when you look at the range of diameters offered.
But the choice here will be simple and quite logical - the diameter of the pipes must be coordinated and determined by the diameter of the connectors of the inputs and outputs of the radiators.
You should not choose less - the coolant in the radiator will unjustifiably stagnate and exert excessive pressure on the fittings.
And a larger diameter is generally useless - the pipes will always be half empty, and excess air is also highly undesirable.
Pipe laying is where you can turn around
To create a heating system with your own hands is a rather complicated matter without the availability of special knowledge and experience. Even a detailed study of the photo and video materials on our site dedicated to this topic will hardly help you - the price of the error is too high.

But to start laying PVC pipes, especially according to a previously developed thorough scheme - is quite a possible thing. This will help you to be closer to this one of the most responsible life support systems in a country house, which was built not only to provide this very life, but also to enjoy life as often as possible.
In our country, metal heating pipes have been installed for a long time in order to achieve high quality operation of the heating system of the premises. In any case, such products will be able to provide reliable circulation of the coolant in a closed network of channels.
Therefore, it is worth considering in more detail the features and characteristics of this product. Individual elements can also act as structural materials.
Positive and negative points
The final characteristics of pipes of this type are directly affected by manufacturing technologies that differ significantly from each other. Today, welded or seamless products are produced.
The first of them are formed from a metal sheet, while the others are stitched from a round ingot on a special machine. In addition, with each method there are certain variations in performance.
List of main advantages
- The main advantage is durability. However, this is true when moving media under high pressure.
- Thermal expansion has a very low coefficient, which makes it possible to reduce the wall thickness.
- Almost one hundred percent oxygen and gas tightness, which allows the successful use of elements in closed communication systems.
- Thermal conductivity is an advantage only when installed for heating homes. In the case of cold water, this becomes a disadvantage.
- Affordable price also applies to positive aspects.

Enumeration of constraints
- Exposure to corrosion, as a rule, leads to a decrease in the operating period.
- Weak resistance to aggressive environments and electrical conductivity are also considered negative factors.
- Poor flexibility of components; therefore, many connecting parts are required.
- The relatively large mass makes installation more problematic. In addition, certain knowledge is needed to carry out the work.
Conclusion! After mentioning the positive and negative factors, we can come to the conclusion that metal pipes are quite suitable for heating systems, since the disadvantages in this case are relative.
Alloy species
When heating is made of metal pipes, the type of a product is taken into account when choosing, depending on the chemical compounds in the production of the substrate. Thus, completely different materials can be taken to create the final product.

Cast iron
It is an alloy based on iron, from which in the molten state it is possible to make all kinds of castings without special difficulties. It has similar characteristics to steel, but has a high carbon content.
If necessary, its properties are improved by heat treatment for malleability.
- Special joints equipped with a sealing collar are installed at the joints, so that installation is carried out in a short time.
- To increase the corrosion resistance, a protective film is applied to the inside and outside.
- In the assortment there are usually products whose diameter ranges from 50 to 300 millimeters.
Addition! Unlike plastic analogues, cast iron products have the highest level of mechanical strength, as well as resistance to high temperatures.
Steel
Such products are afraid of corrosion, so even during manufacture they can undergo additional processing that can increase resistance to external influences (see also article about). Hot galvanizing is widespread when a separate element is placed in a special bath.
During installation work, the connection is carried out in several ways:

- Docking using threaded couplings or special fittings. Impermeability is achieved thanks to the gasket. When working, the usual installation instructions can be used.
- Flange connection when fasteners with a bolt lock are installed on the edges of the elements.
- Autogenous welding.
Note! To create pipes, stainless steel is often used, which includes the main additive - chrome. Other components are also added (titanium, nickel, and so on).
Copper
To all these advantages it is necessary to add durability, which can reach huge intervals of time. Products for engineering networks without welding are almost made of pure copper. First, the elements are extruded, after which lamination and broaching are performed.
There are two types of such pipes:
- The first of them are made of copper, which has been hardened for hardening. Usually this is a general purpose product with a diameter of 22 to 54 mm. Delivery is carried out by cutting bars.
- Other products are made of boiled copper, therefore they are more malleable and technologically advanced. Their diameter ranges from 6 to 22 mm. In most cases, delivered in bays.

Note! Such pipes are joined together mainly by welding or soldering, when the filler metal penetrates into the space between the sleeve and the heated edges of the product.
As a complement
Therefore, it is necessary to approach the assembly process with a set of basic knowledge and at least elementary skills in construction. It is advisable to fully understand the video and photo materials.
If you started to think about how to make heating in your new home, then this article will be useful to you! The starting point for us will be the calculation of the heat loss of those rooms that we are going to heat. Such a calculation can be ordered from a professional designer (it makes sense for large cottages and production facilities), or done using it. After calculating the heat loss, you need to proceed to the selection of the boiler
Choosing a boiler for the home.
Example: heater, for boiler
Next, you need to decide which boiler you need. This difficult choice is made on the basis of which fuel is cheaper and more convenient for you to heat your home. For some regions, such fuel will be coal, for others, electricity or natural gas. However, we live in Russia and it may happen that your gas or light is turned off. Therefore, in order not to be left without heat in the winter, you need to duplicate your system - ideally for a private house, I recommend installing an electric, and if there is gas, gas gas boiler. You can argue that it will be expensive, but if you install only one boiler, for example a gas one, and in the winter you will freeze the chimney and because of this the boiler heat exchanger will defrost, then you will have to evacuate somewhere during the repair.
To avoid such disasters, it is necessary to install not one, but at least two boilers. If one heating device fails, you turn on the other and can repair the failed one. Often the following “combination” of boilers is used - or a gas boiler plus a long-burning boiler on coal with a built-in heater block.
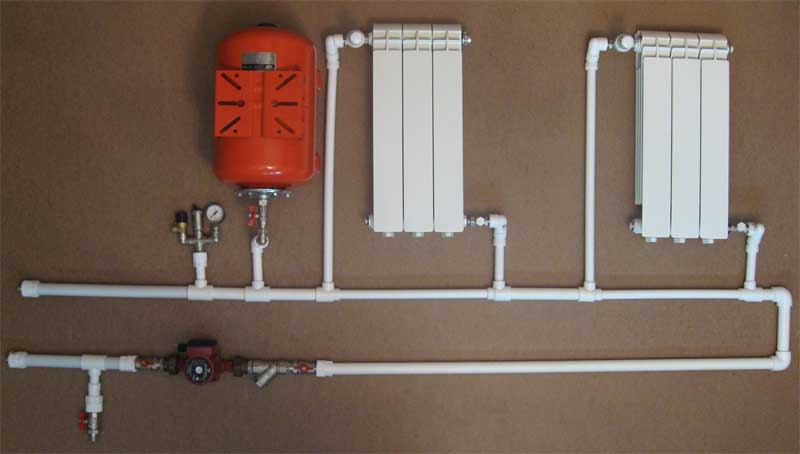
Choosing the type and configuration of the heating system.
It is necessary to think over the configuration of the heating system in advance. By the word "configuration" I mean the structure of the system, that is, you need to decide on the layout of the piping, the location of the heating devices, the installation location of the boiler and boiler equipment. And you need to decide what type of heating system you will use - radiators or radiators plus a warm floor. The last option of the heating system is a special case combined heating system.
Heating systems differ in the way the coolant circulates. There are three types of heating systems for the circulation of the coolant:
- Gravity heating systems - in them the circulation of the coolant occurs due to the separation of the coolant by density as a result of heating in the boiler. Heated water is lighter than cold, so it rises up the feed pipe, and then, using gravity, “pushes” cold water into the boiler. Such a system is non-volatile, but requires a large pipe diameter and compliance with slopes.
- Forced circulation heating systems - The most popular heating systems at the moment. In them, the circulation of the coolant is provided using a special pump. Systems with forced circulation can be made using pipes of small diameters, which significantly reduces the cost of materials and installation. In addition, in systems with forced circulation, the temperature difference between the return flow is less than the gravity ones, and this creates more comfortable conditions for the operation of the boiler heat exchanger.
- Combined circulation heating systems- These are gravity systems on which a pump is installed to improve circulation. Typically, the pump in such systems is set to “bypass”.
Now let's move on to choosing pipes for heating.
The choice of pipes for heating.
The choice of pipes is no less important than the choice of boiler and configuration! You must choose the right material and pipe diameter for your system. First, decide what kind of heating system you need. If you need a system with natural coolant circulation (gravity system), the diameter of the pipe should be 2 or 2.5 inches, and the material of the pipes is better to take ferrous metal - ferrous metal will be much cheaper than copper or polypropylene. The advantage of such a system is its independence from electricity, since the coolant can circulate in the system under the influence of gravity.
Now the most popular heating systems with forced circulation of the coolant. They require a smaller pipe diameter, which saves money. In addition, it is now fashionable to hide pipes in the walls, and with a small diameter it is much easier to do. But it is worth remembering that it is better to brick up into the wall whole sections without press and collet joints. It is necessary to put on a pipe a special corrugation, in which the pipe will be protected from the aggressive effects of the screed and will have a place for thermal expansion.
For heating, you can take pipes of the following types:
- Copper - if you can afford copper heating, this is a very good option. They combine all the advantages of metal pipes and easy installation by soldering (hard or soft). Copper works great at high temperatures (up to 250 ° C) and at high pressure (60 bar or more, depending on diameter)
- Metal-plastic - for heating, metal-plastic 26 and 32 mm in diameter is best suited. For installation, use press fittings. They are crimped on the pipe with a special tool - a press, which can be rented for such work if you intend to do the work yourself or find an installer with such a tool. The working pressure for plastic pipes is 10 bar - for a private house this is enough with a margin, and for an apartment building it is not enough.
- Polypropylene is a very popular material for installation, but it is worth remembering that not all types of polypropylene pipes are suitable for heating installation. For heating systems only reinforced pipes may be used, they can be reinforced with fiberglass, metal foil in the middle layer or in the outer layer. I will tell you my opinion, the best option for heating would be a polypropylene pipe reinforced with foil on the outside. You will have to tinker with it (you need to strip the foil at the joints), but after that there are no problems with it. However, installers do not like such a pipe because of their laziness, it is easier for them to put you a quick pipe with internal reinforcement or fiberglass. In principle, such a heating system will also be installed, but there is a risk that the pipe reinforced with metal inside may delaminate at the junction and leak, and the pipe with fiberglass is designed more for hot water than for heating.
- Pipes from of stainless steel (corrugated) - they can be annealed and unannealed. It is easier to work with the annealed pipe (it holds its shape). Such a pipe is connected using collet brass fittings with silicone o-rings. Entire sections can be hidden inside the walls, but connections cannot be hidden, they must be accessible. For heating, a pipe with a nominal passage of 20 mm is suitable. Smaller pipes can be used for underfloor heating.
- Pipes from the "black" metal - their main advantage is the low price. They can be used if you have a good welder for their installation. They are well suited for gravity heating systems.
Copper pipes for heating
For heating, do not take pipes of small diameter- metal-plastic pipe with a diameter of 16 mm and a polypropylene pipe with a diameter of 20 mm. not suitable for these purposes due to the large hydraulic resistance. A system made of such pipes simply will not work! Using these pipes, you can only make small sections, such as branches from the riser to the radiator or a jumper on the radiator
You need to read the passport for your boiler, it indicates the connection diameter (most often 1.25 or 1.5 inches; for larger capacities, a connection diameter of 2 inches is used). It is impossible to sharply narrow this diameter, that is, it is impossible to connect the boiler directly to the 16th metal plastic. The heater will probably fail. Usually use 2 or 3 different pipe diameters in heating systems, For example, for polypropylene pipes, risers are often made with a pipe of 40 mm, inlets to radiators are made with a pipe of 32 mm. or a 25 mm pipe, and the bypasses on the radiators make a 20 mm pipe. in diameter.
If you have a solid fuel heater installed, then the first 3-4 meters from it must be removed with metal pipesAnd after that it is already possible to use polypropylene or metal-plastic pipes. The reason for this is the high temperatures to which the plastic pipes are not adapted. It is better to discuss the choice of the diameters of the heating pipes with a heating specialist, if you know this. And of course, it is better for this specialist to make you a full-fledged heating system design. Without a project, you will have to trust the experience of the installer, and the installers, like all people, can be wrong.

Polypropylene pipes with external reinforcement
The choice of heating appliances for your home.
Heating devices can be different:
- Radiators of all kinds.
- Wall or floor convectors
- Pipe registers
- Underfloor heating systems.
And we have already said. Read my past publications. Convectors are selected according to the nominal heat flux, which is necessary for heating the room. If you have French windows, you will have to install floor convectors. The craftsmen make the registers of pipes, it is difficult to talk about their parameters since they are made “by eye”. Underfloor heating systems in Russia are used as an addition to radiators or convectors, since underfloor heating can give 50-75 W of heat per square meter of floor, and this will not be enough in our climate. My recommendations remain the same - for private houses and cottages the best option is an aluminum radiator, for a bimetal apartment. If your ceiling height is less than 3 meters, then one section of the radiator will be enough to heat 2 square meters of area. That is, 10 sections are needed for 20 squares.
Selection of valves for heating.
itap vienna ball valve
For heating, it is best to use brass. ball Valves different diameters. Thermostatic valves are installed on the heating devices, which help to control the temperature in the room. Also, in complex large systems, balancing valves are used - they help to equalize the hydraulic resistance of different heating circuits. If this is not done, then in some rooms it will be very hot, and in others it will be cold, because the coolant like electricity always goes along the path of least resistance.
Do not buy cheap valves (valves and taps). They can be made of low quality materials and will not last long. For example, if the body of the ball valve is made of silumin, and not brass, then it is very likely that you will break it when you tighten with a wrench. The best choice, in my opinion, is Italian stop valves. Manufacturers and prices may vary. I advise you to remember a few names:
In addition, if you make heating from polypropylene pipes, then solder ball valves and valves can be used. They are significantly cheaper than brass. It is also better to give preference to foreign manufacturers from Turkey, the Czech Republic and Germany.
The choice of the circulation pump.
This item is relevant if you have a system with forced circulation of the coolant. A separate article has been written on the topic, which I advise you to read
Special attention is required to warm floors! In them, due to the small cross-section of the pipes and the large length of the contours, only forced circulation is possible! To do this, a special unit is installed on the collector of the warm floor - an autonomous circulation group. It includes a circulation pump with a pressure of 6 or 8 meters. A separate post will be written about warm floors, in which we discuss their features.
Uninterruptible power supplies.
Uninterruptible power supplies are necessary so that when the light is turned off, the coolant circulation and the boiler control system (if it is volatile) do not stop working. If you have a wall-mounted gas boiler installed, then such a source is needed. The source power is selected as the total consumed power of the circulation pumps in the system plus the power consumed by the boiler (most often the source power does not exceed 1 kW). Such sources are powered by batteries, the amount of which is determined by the power consumption and the necessary battery life. A separate article on the topic
A very significant advantage of a gravity water heating system is its independence from the availability of electricity. Gravity heating can also be created in a remote cottage based on a non-volatile solid fuel boiler. The system is silent and reliable; it will undoubtedly be in demand in the future.
Extensive experience has been gained in creating gravity-fed heating systems, because previously all water heating was created on the principle of gravity. The system can be created according to the "standard folk scheme" and with your own hands.
The disadvantages are restrictions on power, heated area, the ability to connect additional circuits, at an increased cost for the creation.
Gravity heating is more expensive, about 2 times compared with forced circulation systems, as it requires a large pipe diameter and special boiler placement. The difficulty in creating and the fact that large-diameter pipes should have a common slope, which means that their position is fixed and therefore they often do not fit into the design of the room, clutter the interior.
How gravity system is calculated
You can order thermal and hydraulic calculation from specialists, in licensed organizations, but it will cost a lot. You can do these calculations approximately using known programs or manually.In any case, the velocity of the fluid in the system is not large. The larger the internal diameters of the pipeline and radiators, as well as the boiler, the greater the amount of liquid will pass through them, the more energy can be transferred.
It is important to answer the question - will there be enough energy to transfer the coolant to heat a particular building? This is the essence of the calculations. But if there are no calculations, then you need to turn to the experience of creating such heating and insulation of buildings.
Loss of energy and fluid movement
First, you need to determine the degree of insulation of the building - whether it meets the requirements of regulatory documents. If not, then the power of not only a gravity-flowing system may not be enough ..... It is more expensive to heat a cold building, you need to warm it, and not increase the heating power.
After the building is insulated, you can turn to the experience of creating such systems, from where it is known that the usual limit area of \u200b\u200bgravity heating is 150 sq. M. on each floor of the building, with a distribution of radiators over 2 shoulders on each floor, and the length of the supply pipe of each shoulder should not exceed 20 meters.
A prerequisite for creating a system is the excess of the hot coolant (usually the middle line of radiators is accepted) over the cold (middle line of the boiler heat exchanger).
With longer pipelines, a calculation would be desirable, or you need to put up with it, which might not be enough during the peak of frosts and the system capacity (coolant speed) would make the building hot.
Consider why the performance of the gravity system will depend.
Features of the heating system with natural circulation
The pressure in a gravity flow system will directly depend on the height of the water column with the difference in water densities (temperature difference) and on the very difference in water densities. The pressure formula is given below.
The greater the difference in supply and return temperatures, and the higher the water column with this difference, the faster the water will circulate, the more heat will be transferred, the more reliable the system and a large area can be heated.
The fact is that water cools most significantly in radiators; before them it is considered hot. After radiators, cold water moves along the return to the boiler heat exchanger, where it is heated. Therefore, the lower the heat exchanger is relative to the radiators, the greater the pressure will be in the system.
In addition, the water cools down in the pipe itself leaving the boiler, which means that the higher the hot pipeline is raised, and the longer and more it gives off heat, the greater the pressure.
However, this heat transfer will have low efficiency for heating a house if the hot pipeline is located under the ceiling. It is better if it is along the floor of a heated massandra and is a heating device for it.
It is not right to just make a tall column of hot water, taking out the expansion tank above the roof. We need the greatest height difference at which a temperature difference would occur, and this is easier to achieve by lowering the boiler.
A typical mistake when creating a gravity flow system for 2 floors is to connect radiators on both floors to the same risers. As a result, it will be still cold on the 1st floor when it is already very hot on the 2nd floor. It is correct for the attic to provide a separate independent heating arm with its own control valve.
System Feature:
- the liquid in the gravity system usually cools significantly, due to the low speed of its movement. The difference in supply and return temperatures is often in the range of 25-30 degrees. The temperature regime, for example, is 75 degrees. exit from the boiler and 45 degrees. return flow. Therefore, it is unacceptable to create a circuit with one pipeline with a series connection of radiators. Only the associated and dead end two-pipe wiring diagrams are suitable.
How the coolant (water) moves
From the foregoing, structural features of a gravity heating system also follow.The boiler is located in the pit, in the basement, in any case, it is desirable that its heat exchanger be below the middle line of the radiators.
All pipelines are made with a general bias in the direction of the fluid:
- water from the boiler rises along the vertical riser to the highest point;
- from a vertical hot riser should always be down to the entrance to the boiler;
- the height difference between the start and end points of the pipe is at least one percent, but the slope along the length can vary as you like;
- it is always best to ensure maximum slope.
Which pipes to use
The diameter of the pipes must be at least 32 mm for supply and return on one wing of the pipeline, while radiators can also be connected with pipes with an internal diameter of 20 mm. And for the riser and feed to the wing - at least 50 mm. However, no one forbids increasing these diameters, which will only make the system more powerful.Until now, conventional steel pipes are considered the optimal variational. With large diameters, they become competitive with plastic. Besides steel pipe large diameter is itself a heating device, due to the significant conductivity of heat by metal.
Boiler, radiators, piping
A special boiler (both gas and solid fuel) with its own small hydraulic resistance is used, designed for a gravity-fed system.Radiators with low hydraulic resistance are used, with a large diameter of the internal holes - usually either cast iron or aluminum.
At the highest point of the pipeline, a valve for bleeding the air is installed (pressure system with a closed expansion tank (hydraulic accumulator)). A safety group is built into the system at the outlet of the boiler - a pressure gauge and an emergency valve. Or at the highest point there is an open expansion tank.
The drain valve is located in the boiler area at the lowest point of the pipeline, a drain is made either to the sewer or to the tank.
Selection of the boiler according to power is carried out as usual - depending on the heat loss of the building, and radiators - on the heat loss of each room where they are installed.
At the same time, they often use the rule - radiators are in total slightly more powerful than the boiler (taking into account that the nameplate temperature of the liquid is usually higher than real, i.e. radiators are purchased even more powerful by 20 - 35%), after which the total power of the radiators is distributed across the rooms.
One-wing gravity heating schemes
Typical water heating scheme with gravity flow of fluid. There is only one wing. The hot pipeline is located higher, risers go down from it to each radiator or a pair of radiators. The diagram shows the expansion tank instead of the accumulator.
In practice, often such schemes are implemented so that the expansion tank, the upper pipeline would be located in the attic, and the return line often falls under the floor into the basement. At the same time, pipelines clutter up living space less and do not spoil the interior. But then all pipelines in the cold zone should be well insulated - a layer of at least 15 cm of mineral wool. Polyfoam is not suitable, as it is eaten by rodents and should not be heated to 70 degrees.
Laying pipes in the attic

A sub-option of this scheme - the return is raised up, since it is not always possible to lay it down - doorways interfere, there is no basement, etc.
In a small house

The option of placing radiators right next to the boiler. This is possible only in climatic zones with a constant positive temperature, and if the windows are sufficiently insulated (double-glazed windows), and there is no particular need to create thermal curtains by placing radiators under the windows. The scheme is used when it is not possible to lower the boiler level - pipelines are reduced as much as possible.
Two-wing pipeline

The following example is more in demand in life. More often than not, pipelines are located during the gravity flow of liquid in a small private house or at the cottage at the level of radiators with a general bias shutter speed.
The pipeline is divided into two wings, which it is desirable to make the same length. All radiators are connected through valves to quickly adjust the flow of water.
For two floors

Another example of the "life" of piping during gravity fluid movement. This time, a full floor and an attic are heated.
Since the wing of the attic is low-power, it is turned on by a pipeline of a smaller diameter - 25 mm. Here, risers are used for each pair of radiators in the rooms of the first floor, and the hot pipeline is laid along the attic floor and is a heating element for it.
The scheme requires the creation of sufficient pressure, so the boiler heat exchanger is located at least half a meter below the center line of the first floor radiators.
Principles and Conclusions
You can develop any number of gravity heating schemes, depending on the specific layout of the house, but the following principles are always observed - the largest column of water with a temperature difference, the maximum pipe diameters and special boilers and radiators, the pipe ring - “feed-radiator-return” are made as short as possible , for which the pipeline is divided into several arms, which are connected to the boiler in parallel.It is also important: - if gravity heating in the house was created independently, or the owners took an active part in its creation, then all the identified shortcomings during the operation can be corrected with your own hands or the system can be modified without any special costs if its shortcomings are identified.
